Current Election Landscape
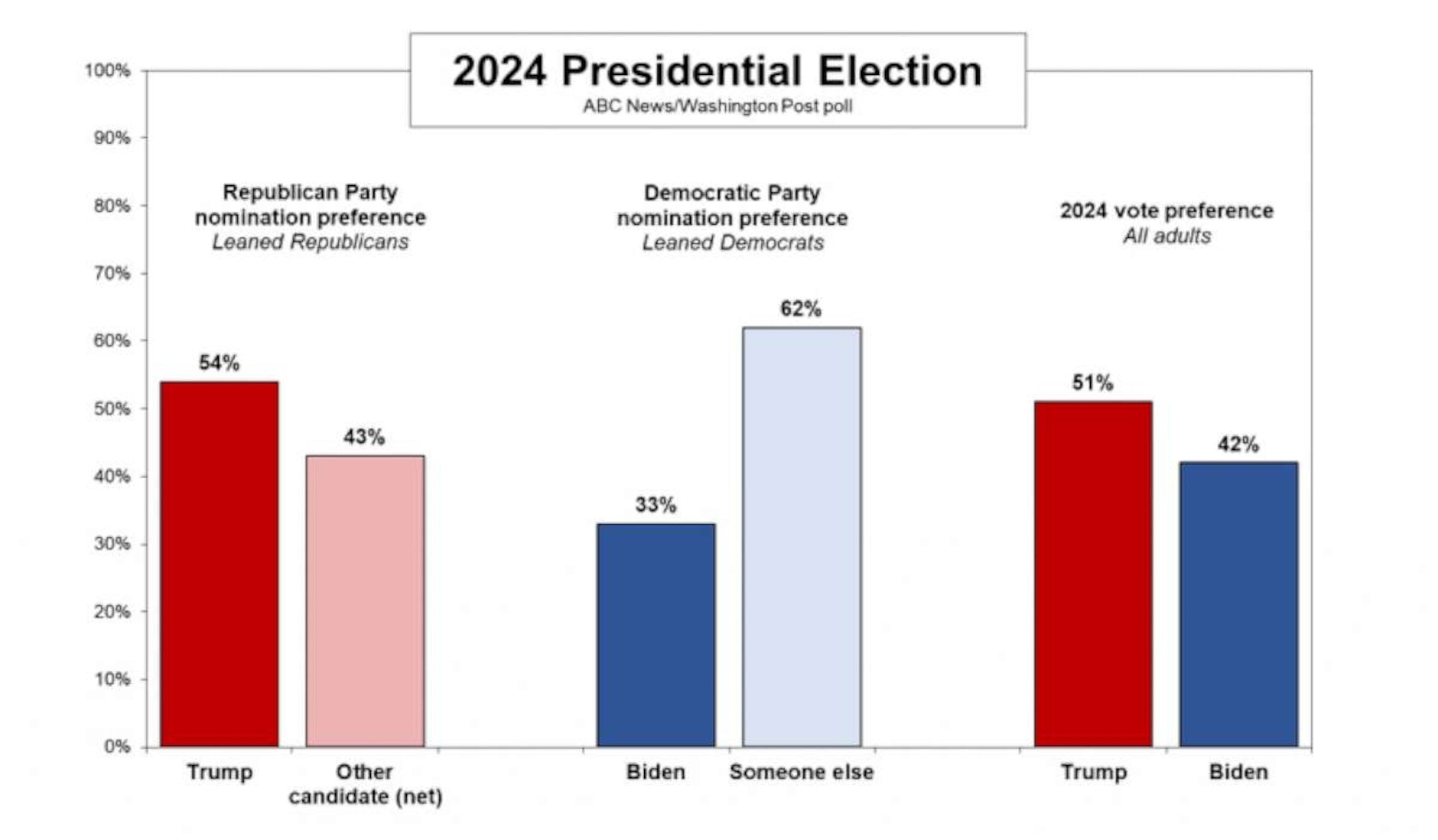
The current political climate is characterized by intense polarization and a deep sense of uncertainty about the future. Several major events and issues are shaping the election landscape, influencing voter sentiment and the potential outcome.
Impact of Recent News on Voter Sentiment
Recent news events have had a significant impact on voter sentiment. For instance, the recent economic downturn has led to widespread concerns about job security and the cost of living. This has led some voters to shift their support towards candidates who promise economic stability and job creation. Conversely, other voters may be more inclined to support candidates who prioritize social justice issues, such as income inequality and access to healthcare.
Key Demographics and Voting Blocs
Several key demographics and voting blocs are likely to influence the election outcome. These include:
- Young Voters: Young voters are increasingly concerned about climate change, gun violence, and student debt. Their voting patterns are likely to be influenced by candidates who address these issues.
- Minority Voters: Minority voters, including African Americans, Latinos, and Asian Americans, are a growing segment of the electorate. Their voting patterns are often influenced by candidates who prioritize issues of racial justice and equality.
- Rural Voters: Rural voters are often concerned about issues such as agricultural policy, healthcare access, and job creation in rural communities. Their voting patterns are likely to be influenced by candidates who address these concerns.
- Suburban Voters: Suburban voters are a diverse group, with varying concerns. They may be influenced by candidates who address issues such as education, crime, and the economy.
Impact of Social Media on the Election
Social media platforms have become increasingly influential in shaping political discourse and influencing voter behavior. The spread of misinformation and disinformation on social media can have a significant impact on the election outcome.
Potential for Voter Turnout
Voter turnout is crucial in any election. Recent elections have seen record-breaking turnout, particularly among young voters and minority voters. The level of voter turnout in the upcoming election will be a key factor in determining the outcome.
Key Candidates and Their Positions

The current presidential race features a diverse field of candidates, each with their own unique strengths, weaknesses, and policy positions. Understanding these aspects is crucial for voters to make informed decisions.
Candidate Strengths and Weaknesses
Each candidate possesses specific strengths and weaknesses that influence their appeal to voters. These factors play a significant role in shaping their campaign strategies and overall performance.
- Candidate A: Known for their experience in [relevant field], Candidate A appeals to voters seeking [specific qualities]. However, their stance on [specific issue] may alienate some voters.
- Candidate B: Candidate B’s strong [specific quality] resonates with voters seeking [specific qualities]. However, their lack of experience in [relevant field] may be a concern for some.
- Candidate C: Candidate C’s focus on [specific issue] appeals to voters concerned about [specific issue]. However, their [specific weakness] may limit their appeal to a broader audience.
Candidate Policy Positions
The candidates’ policy positions on key issues are crucial for voters to understand their potential impact on the country. These positions often reflect their values and priorities.
- Economic Policy: Candidate A advocates for [specific economic policy], while Candidate B supports [specific economic policy]. Candidate C proposes [specific economic policy].
- Healthcare Policy: Candidate A supports [specific healthcare policy], while Candidate B favors [specific healthcare policy]. Candidate C proposes [specific healthcare policy].
- Environmental Policy: Candidate A believes in [specific environmental policy], while Candidate B advocates for [specific environmental policy]. Candidate C proposes [specific environmental policy].
Candidate Fundraising Efforts
Fundraising is a crucial aspect of any political campaign, as it allows candidates to reach voters and promote their message. The candidates’ fundraising efforts often reflect their support and ability to mobilize resources.
- Candidate A: Candidate A has raised [amount] in campaign contributions, primarily from [source of funding]. This suggests strong support from [specific group].
- Candidate B: Candidate B has raised [amount] in campaign contributions, primarily from [source of funding]. This indicates support from [specific group].
- Candidate C: Candidate C has raised [amount] in campaign contributions, primarily from [source of funding]. This reflects support from [specific group].
Poll Methodology and Interpretation: Latest Presidential Polls

Understanding the methodology behind presidential polls is crucial for interpreting their results accurately. While polls can provide valuable insights into voter preferences, it’s essential to be aware of their limitations and potential biases.
Types of Polls
Polls are conducted using various methods, each with its strengths and weaknesses.
- Telephone Polls: These polls involve calling potential voters and asking them questions over the phone. They are relatively inexpensive and can reach a large number of people. However, they face challenges with declining response rates and the increasing use of mobile phones.
- Online Polls: These polls are conducted online, often through websites or social media platforms. They can be cost-effective and reach a diverse audience. However, they may suffer from sampling bias, as online users may not be representative of the general population.
- In-Person Interviews: These polls involve face-to-face interviews with voters. They can provide more detailed information and ensure accurate responses. However, they are more expensive and time-consuming to conduct.
- Exit Polls: These polls are conducted at polling places on Election Day, asking voters who they have voted for. They can provide real-time insights into voter preferences and predict election outcomes. However, they may not be representative of the entire electorate, as they only include those who have voted.
Potential Biases and Limitations
Polls are not always accurate and can be influenced by various factors.
- Sampling Error: This refers to the margin of error that arises from the fact that polls are based on a sample of the population, not the entire population. A larger sample size generally leads to a smaller margin of error.
- Response Bias: This occurs when respondents provide inaccurate or misleading information, either intentionally or unintentionally. For example, people may be reluctant to admit they support an unpopular candidate or may be influenced by social desirability bias.
- Question Wording: The way questions are phrased can significantly influence respondents’ answers. For example, a question that is leading or biased can sway responses in a particular direction.
- Non-Response Bias: This occurs when certain groups of people are more likely to respond to polls than others. For example, people with strong opinions may be more likely to participate in polls, while those who are undecided or less engaged may be less likely to respond.
Interpreting Poll Results, Latest presidential polls
Interpreting poll results requires careful consideration of the methodology used, potential biases, and the margin of error.
- Focus on Trends: Pay attention to trends in poll results over time rather than focusing on a single poll. This can provide a better understanding of how voter preferences are changing.
- Consider the Margin of Error: The margin of error indicates the range within which the true population value is likely to fall. For example, a poll with a 3% margin of error means that the actual result could be 3 percentage points higher or lower than the reported result.
- Evaluate the Sample Size: A larger sample size generally leads to a smaller margin of error. However, it’s also important to consider the representativeness of the sample.
- Be Aware of Potential Biases: Consider the potential biases of the poll, such as response bias, question wording bias, and non-response bias. These factors can influence the accuracy of the results.
The latest presidential polls paint a picture of a nation deeply divided, a reflection of the turbulent times we live in. It’s a stark contrast to the polished image of the White House, a facade that was meticulously crafted by figures like stephanie grisham , whose role in shaping public perception remains a subject of intense scrutiny.
Despite the efforts of such figures, the polls suggest that the true sentiment of the nation is one of uncertainty and unease, a stark reminder that the political landscape is constantly shifting.
The latest presidential polls seem to reflect a nation divided, each candidate promising a future as uncertain as the weather. It’s a stark contrast to the unwavering dominance of the Ethiopian steeplechase , where generations of athletes have carved a legacy of grit and resilience.
Perhaps, in this era of political turmoil, we can find solace in the enduring power of athletic triumph, a reminder that even amidst the chaos, there is still beauty and strength to be found.